Data Architecture
Data architecture is composed of models, policies, rules or standards that govern which data is collected, and how it is stored, arranged, integrated, and put to use in data systems and in organizations.Data is usually one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture or solution architecture. A data architecture should[neutrality is disputed] set data standards for all its data systems as a vision or a model of the eventual interactions between those data systems. Data integration, for example, should be dependent upon data architecture standards since data integration requires data interactions between two or more data systems. A data architecture, in part, describes the data structures used by a business and its computer applications software. Data architectures address data in storage and data in motion; descriptions of data stores, data groups and data items; and mappings of those data artifacts to data qualities, applications, locations etc.Sample Architecture
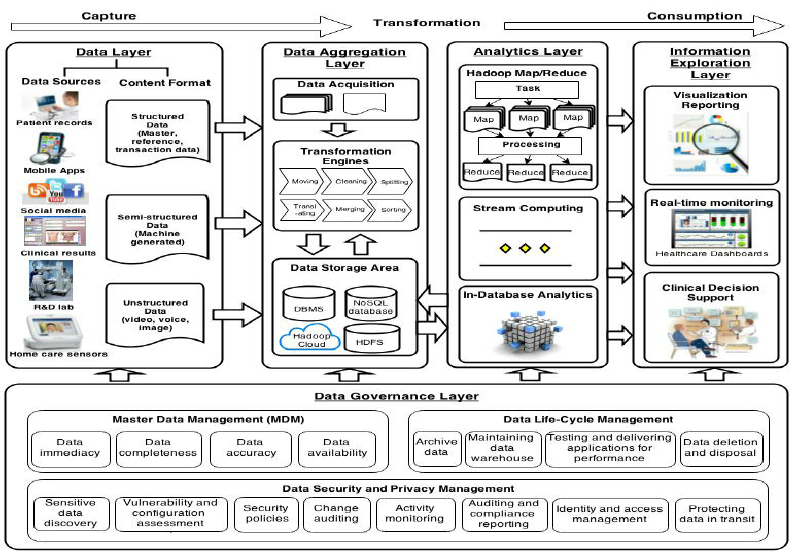
Source Structured Content
The term structured data generally refers to data that has a defined length and format for big data. Examples of structured data include numbers, dates, and groups of words and numbers called strings. Most experts agree that this kind of data accounts for about 20 percent of the data that is out there. Structured data is the data you're probably used to dealing with. It's usually stored in a database.Although this might seem like business as usual, in reality, structured data is taking on a new role in the world of big data. The evolution of technology provides newer sources of structured data being produced - often in real time and in large volumes. The sources of data are divided into two categories:
Computer or machine-generated: Machine-generated data generally refers to data that is created by a machine without human intervention.
Human-generated: This is data that humans, in interaction with computers, supply.
