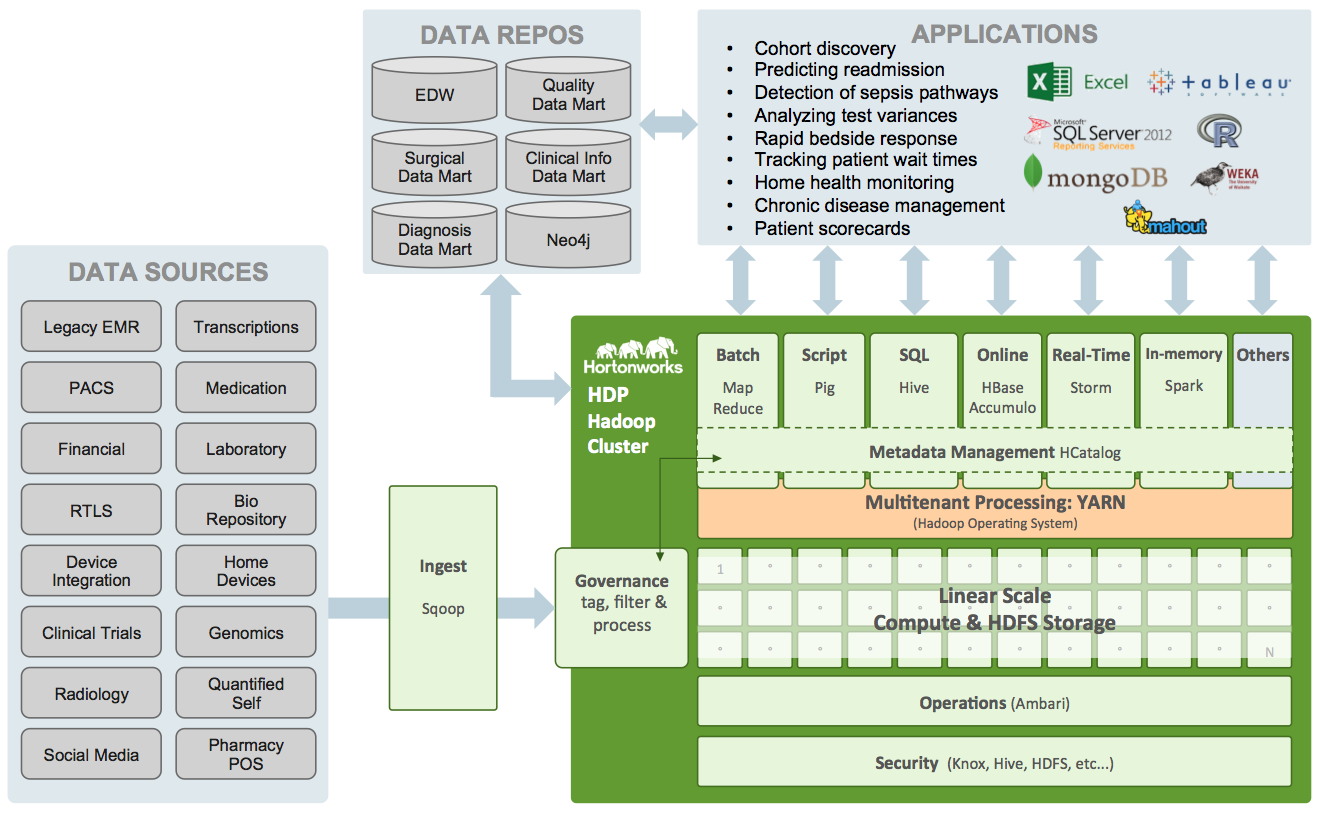
Health
Big Data has changed the way we manage, analyze and leverage data in any industry. One of the most promising areas where it can be applied to make a change is healthcare. Healthcare analytics have the potential to reduce costs of treatment, predict outbreaks of epidemics, avoid preventable diseases and improve the quality of life in general. Average human lifespan is increasing along world population, which poses new challenges to today's treatment delivery methods. Health professionals, just like business entrepreneurs, are capable of collecting massive amounts of data and look for best strategies to use these numbers. In this article, we would like to address the need of big data in healthcare: why and how can it help? What are the obstacles to its adoption? We will then provide you with 12 big data examples in healthcare that already exist and that we benefit from.Sample Architecture